Need multiple shell sessions?
You are logged into your remote server via SSH and happily plucking along at your keyboard and then it happens. Suddenly, the characters stop moving and then you get the dreaded “Connection Closed” message. You have just lost your session. You were halfway through some task and now you have to start over. Ugh. Well you can prevent this from happening by using screen.
Lost your shell connection?
The Linux screen tool can not only save you from disconnection disasters, but it also can increase your productivity by using multiple windows within one SSHsession.
What is Screen for Linux?
As the man page states, “Screen is a full-screen window manager that multiplexes a physical terminal between several processes (typically interactive shells).” This can be a life saver when working on your dedicated server. Screen has a several great features for helping you administer your server more productively and safely.
Installing Screen on Linux
Chances are that you already have screen on your system. On most Red Hat distributions you can find it in /usr/bin/screen.
[root@arun01-I84076 /]# which screen
/usr/bin/screen
If you do not have screen, then you can install it easily from an RPM or the package file for your system. On Cobalt Raq servers, you can safely use the RedHat RPMS appropriate for your system.
Screen RPMs: rpmfind
Screen Web site: GNU Screen
Screen RPMs: rpmfind
Screen Web site: GNU Screen
Using screen Command in Putty
[root@arun01-I84076 /]# man screen
1.To enter into screen type screen command in putty window
[root@arun01-I84076 /]# screen
2.To view the screen help press ctrl+A then ?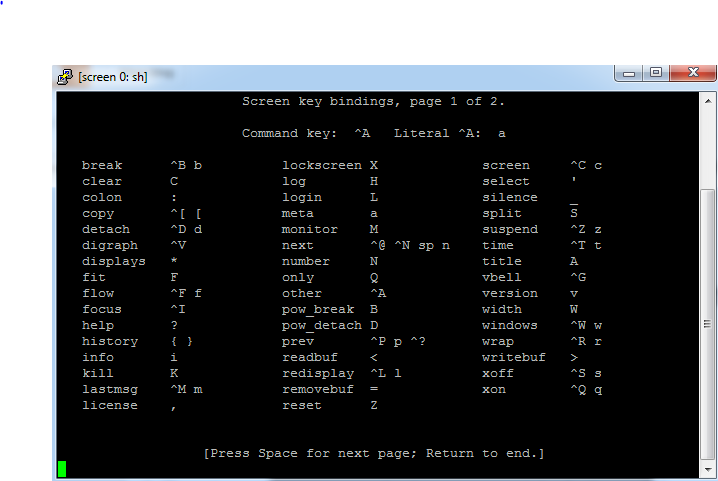
Enter q to exit from help window
3.To create a new screen press ctrl+A and hit "c" to create new screen.
4.Now you can perform what ever installation you need and press ctrl+A and hit "d" to detach from screen.
5.You can toggle to several windows by ctrl+A
6.To know what are the screens available
2.To view the screen help press ctrl+A then ?

Enter q to exit from help window
3.To create a new screen press ctrl+A and hit "c" to create new screen.
4.Now you can perform what ever installation you need and press ctrl+A and hit "d" to detach from screen.
5.You can toggle to several windows by ctrl+A
6.To know what are the screens available
sh-3.2# screen -list
There are screens on:
17457.pts-1.arun01-I84076 (Attached)
17894.pts-3.arun01-I84076 (Attached)
4 Sockets in /var/run/screen/S-root.
7.To get back from screen press ctrl+D
8.If you login as new session then you can attach your screen by
[root@arun01-I84076 ~]# screen -r 18454.pts-7.navve01-I84076


Thanks for giving the tips. You can also try Go4hosting to experience best hosting services.
ReplyDelete